Though many people consume alcohol in moderate amounts as part of their routine lifestyle, it is not usually considered healthy. The cause of this mixed reputation of alcohol is due to the long-term and short-term effects it causes on your general health and various organs of the body, such as liver, brain etc. However, what are the effects of alcohol on your teeth, gums and tissues of mouth?
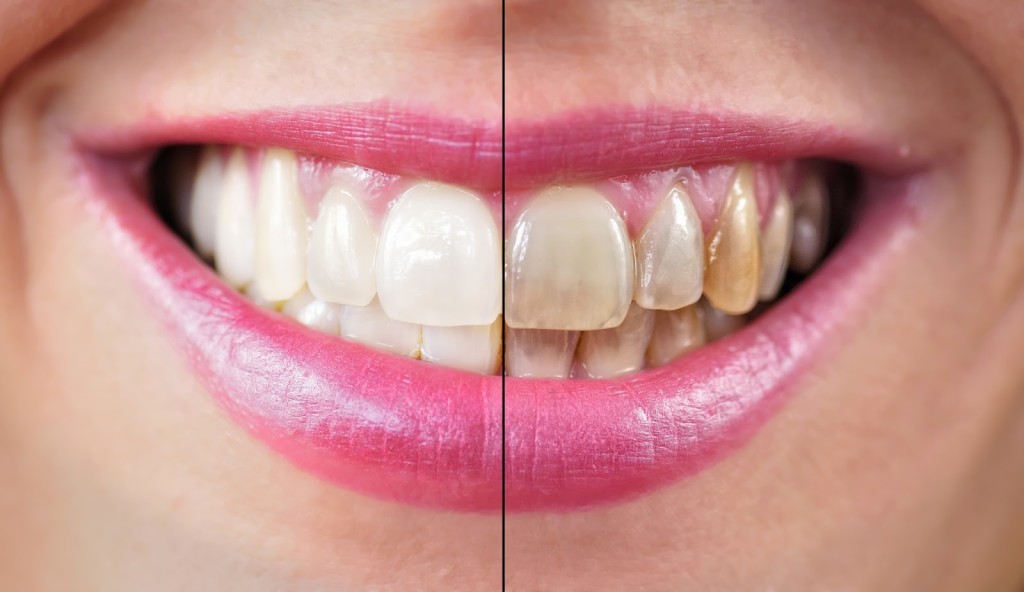
Effects of Alcohol on Teeth and Mouth
- The sugar in alcohol makes you prone to tooth decay: Sugar increases the risk of developing tooth decay as the bacteria present in your oral cavity thrives on sugar. Some amount of sugar is present in all types of alcoholic drinks but certain types contain more sugar than others such as Sherries, liqueurs, fortified wines and ciders. Hence, limit intake of drinks which have high sugar content; instead choose drinks which have less sugar such as ales and white wines.
- Acid present in alcoholic cocktails erodes your teeth: When alcohol is mixed with acidic drinks such as energy drinks, fruit juices and soda, the acid present in this cocktail erodes your teeth (alcohol teeth). If you drink several such drinks, your tooth enamel will gradually get eroded making your teethsensitive to hot and cold, dark in color and prone to decay.
- It can cause staining of your teeth: Alcoholic beverages that are heavily colored such as sangria and red wine can cause staining of your teeth. Your teeth can also get stained by consuming alcoholic beverages that contain tea and coffee. To prevent staining of your teeth, drink water in between alcoholic drinks that are known to cause teeth staining so as to help remove the stain causing dyes from the surface of your teeth.
- It can cause dehydration which makes you prone to tooth decay: Alcohol can cause dehydration of your body. You require sufficient quantity of saliva in your oral cavity to remove harmful bacteria from attacking your teeth. However, when your body is dehydrated after consuming alcohol, far less quantity of saliva is being produced, raising your risk of tooth decay.
- It leads to disease of the gums: Alcohol makes you more prone to develop gum diseases in the following ways: bacteria thriveon the sugar present in alcoholic drinks; drinking alcohol is associated with nutritional deficiencies and alcohol consumption causes dehydration, which leads to decreased production of saliva making you more prone to tooth decay (alcohol teeth). Furthermore, alcohol irritates gum tissues and people who abuse alcohol have poor habits of dental hygiene. This increases the risk of gum diseases, ranging from swelling of gums to developing dangerous infections.
- It increases risk of oral cancer: Alcohol drinking is not all fun and entertainment. Excessive consumption of alcohol makes you prone to develop oral cancer and according to estimates, it is the second largest risk factor. Alcohol can corrode your cheeks, gums and skin, leading to cancer of the oral cavity and throat. In combination with smoking, excessive drinking increases the risk of developing cancer manifold. Alcohol causes dehydration of the cell walls, allowing the carcinogens present in tobacco to enter the cells in your oral cavity more easily. The nutritional deficiencies associated with heavy drinking also reduce the ability of your body to fight cancer.
How to Minimize the Effects of Alcohol on Teeth
Though some of you can quit alcohol; however, for some it becomes a want or necessity in life. Certain helpful tips to decrease the effects of alcohol on teeth are described below:
- Sip your alcoholic drink by a straw. This minimizes the contact of the liquid with your teeth and gums as the liquid flows directly into your mouth.
- While you are drinking, rinse your mouth often with water. Carry a bottle of water with you so that you can flush your mouth and remove the substances left by alcohol in your mouth.
- Chew gum (sugar-free). Chewing produces saliva; this helps in cleaning your mouth by killing bacteria and flushing away substances left by alcohol from your mouth.
- Do not use mouthwash or brush your teeth for at least one hour after you had a drink. Your body is already controlling and processing the influx of acid (present in alcohol) in your oral cavity; swishing mouthwash or brushing teeth will make your tooth enamel softer as you will add more acid into the mixture.
- Visit your dentist regularly. By doing so, you can combat the adverse effects alcohol has on your teeth (alcohol teeth) and also resolve any new problems that may have developed in between. Your dentist can fill a tooth cavity or do teeth whitening. You can also enquire about methods of how to quit alcohol.
A Comparison of the Common Alcohol Drinks
White Wine: When you are sipping white wine for long duration, your mouth does not get time to return to its original pH. The acidity of the wine softens enamel of the teeth, making them more prone to eroding or getting stains from other drinks or foods.

Cocktails and Mixed Drinks: Rum and cola. Consuming a delicious cocktail may help you relax; however, ingesting these drinks, which have high sugar content, regularly can have terrible effects on your teeth. The more the acid present in your drink, for instance, whiskey mixed with cola, the quicker your teeth will be damaged. Moreover, if you are consuming these drinks on a regular basis, you are keeping these acidic, sugary liquids for a significant amount of time in your mouth.

Red Wine: Red wine is bad for your alcohol teeth. It is not only acidic but also has dark pigments called chromogens. Moreover, it also contains tannins, which has a binding effect. Hence, if you love dark red wine, you should be aware that the darker it is, the more your teeth are at risk of getting stained.
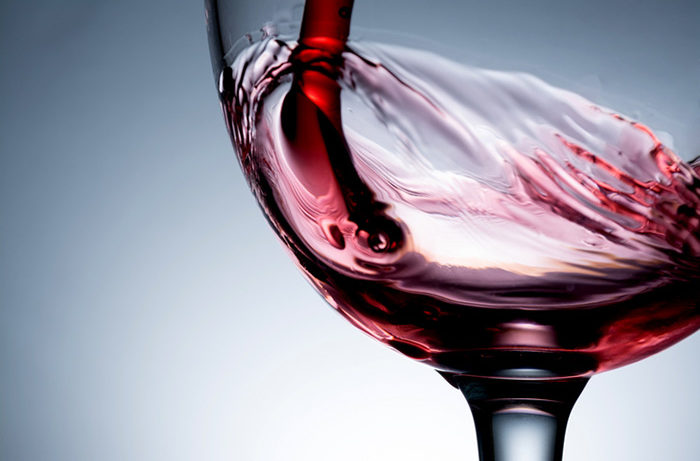

Spirits: Drinks that have high alcohol content, for instance, rum, whiskey and vodka are bad for tooth enamel. Moreover, they reduce production of saliva, making it difficult to naturally flush away acids and bacteria.
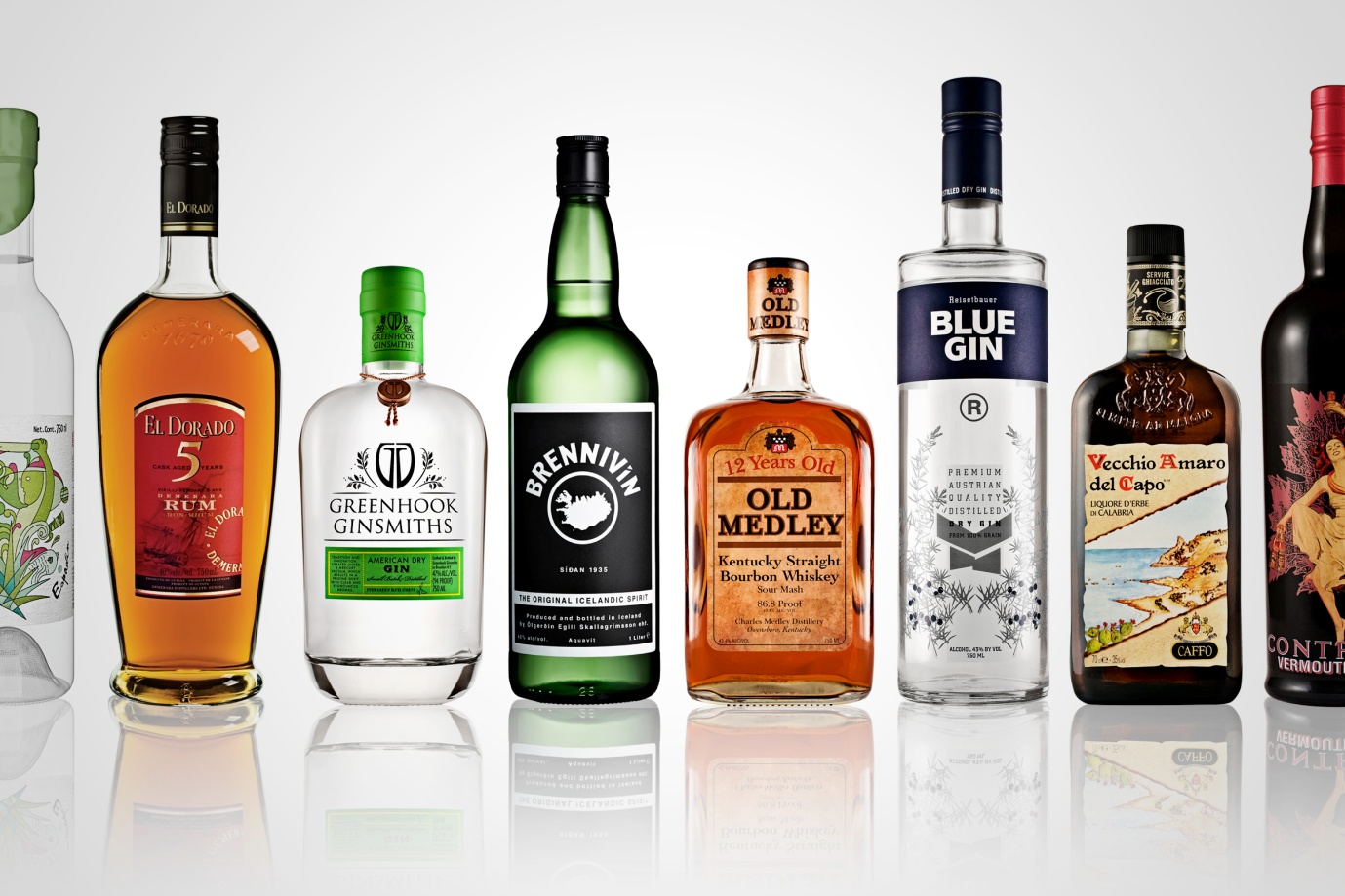

Beer: Beer is acidic; hence, it can be harmful to your teeth if consumed for long duration. Moreover, dark beers can cause staining of your teeth. However, of all types of alcohol, a low-carb, light beer is best for your teeth, as its acidity is the lowest and water content is the highest.
