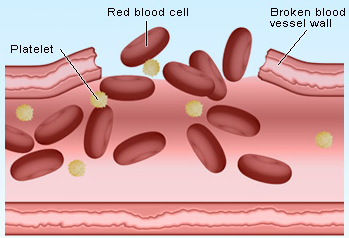
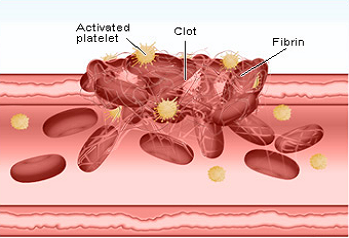
Platelets are part of the components in your blood. They contain a number of compounds and granules that work to clot the blood when an injury occurs. These platelets have a life span of 10 days and they constantly regenerate. Your platelet count is largely influenced by factors such as racial orientation and exercises you engage in.
What Does Low Platelets Mean?
Thrombocytopenia is a medical term that is used to describe low platelet count. A low platelet count could be as a result of various factors. The patient could have a medical disorder that affects the immune system, leukemia or it could also be brought about by certain medications. Most cases of thrombocytopenia are mild but other cases could be fatal, especially when the patient has a dangerously low platelet count. This is because abnormally low platelets could cause internal bleeding.
Usually, a blood count is conducted to determine the patient’s platelet count. In normal circumstances, a normal blood count would reveal between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets for every micro liter of blood. This would mean that a low platelet count would constitute less than 150,000 platelets.
What Causes Low Platelets?
Like we mentioned above, thrombocytopenia has various causes and these include:
1. Reduced Platelet Production
The body continuously produces blood cells from the bone marrow. Reduced production could be due to illnesses such as anemia and leukemia which affect the bone marrow. Viral infections such as HIV could also be responsible as they reduce the ability of the bone marrow to generate platelets. Excessive consumption of alcohol, chemotherapy and toxic chemicals could also reduce the production of platelets.
2. Platelets Trapping in the Spleen
Sometimes, the spleen could be responsible for the low platelet count. As we all know, this is the smallest organ in the body and it works to filter the blood from unwanted components as well as fight infection. When the spleen is enlarged, it decreases the number of platelets as it tends to hoard on them.
3. Abnormal Platelet Breakdown
In other cases, the body may be responsible for destroying or using up the platelets at a rate that is faster than the production rate. This could be due to pregnancy or ITP also known as Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura which is a condition where the immune system attacks the platelets. Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are also likely causes. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) is a condition which is characterized by the sudden formation of small blood clots in the body leading to enhanced usage of platelets. Other causes could be bacterial infections, hemolytic uremic syndrome which is a rare condition that leads to the destruction of red blood and brings about a sudden decrease in the platelet count. Certain medications may cause a decrease the number of platelets in the blood.
What Are the Symptoms and Complications of Low Platelets?
There various tell-tale signs that indicate a low platelet count. These include superficial bleeding that appears like a rash. This is usually evident in the legs. You could also experience profuse bleeding even with minor cuts or easily bruise which indicates that your blood does not clot as it should. Abnormal menstruation is also a sign of low platelets and another major sign would be frequent nose bleeds and bleeding gums. Blood in the stool or urine is never a good sign and could indicate insufficient platelets.
Thrombocytopenia comes with fatal complications and this depends on the extent of the low platelets. If the patient’s platelet count is lower than 10,000, internal bleeding could easily occur. Major complications are rare but deadly. Severe cases of thrombocytopenia could lead to internal bleeding in organs such as the intestines or the brain.
How is Low Platelets Treated?
The treatment for low platelet is largely dependent on the platelet count
1. Mild Thrombocytopenia
Mild thrombocytopenia could heal in its own. A good example is pregnancy which could bring about low platelets. In such cases, the platelet count could improve when the woman gives birth. Mild cases do not necessarily require treatment.
2. Severe Thrombocytopenia
Severe thrombocytopenia requires medical attention and this is because it could be brought about by certain illnesses. Usually, the doctor will try to identify the underlying condition. In other cases, blood transfusions may be required. Blood transfusions help replenish the blood with platelets or red blood cells. If the cause of the low platelets is ITP, the spleen could be removed surgically. The doctor may treat the condition with medications that suppress the immune system so as to prevent antibodies from attacking the platelets.
3. Home Remedies
There are various actions you can take on your own to help increase your platelets.
- Lifestyle changes could help and you may want to reduce your alcohol intake. Alcohol slows down platelet production and it’s advised that the patient reduces their alcoholic intake. You can also avoid alcohol altogether.
- Over-the-counter pain medication such as ibuprofen, aspirin, Advil and others can have an effect on the production of platelets. Use caution when taking such medication, take them in moderation and only when needed. Also avoid self-diagnosis.
- You could also refrain from activities that could easily cause injury. Sports with high contact such as football, boxing, basketball and rugby come with high injury risks. It’s important to ask your doctor for advice on the kind of sports that are safe to engage in. Non-contact sports such as skiing and activities such as horseback riding are also not advised.
If you suspect for any reason that you have low platelets, you need to keep track of the symptoms. You can write them down, list any kind of medications you may be taking and basically be aware of unusual changes in your body such as an increase in the number of injuries.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice that you easily get bruises, injuries, heavy menstrual flows and other symptoms such as spotting in the urine and the stool, you need to seek medical attention. Profuse bleeding from minor cuts is not normal and bleeding that seems to be continuous even after applying first aid techniques is not a sign of good health. Seek medical attention when you have any of the symptoms we mentioned above.