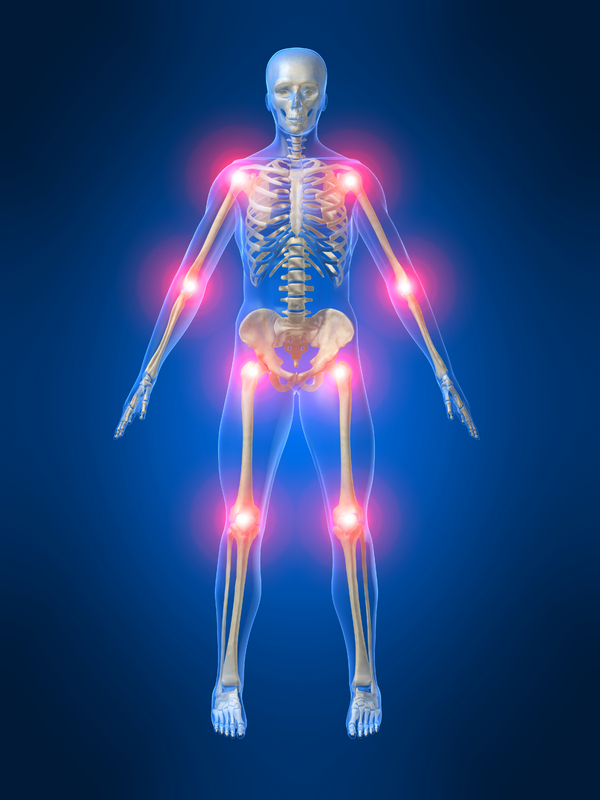
Joint pain, occasionally referred to as arthralgia or arthritis, can arise from any area where two or more bones meet. Sometimes this pain is mild, causing you to feel discomfort when the joint moves, but it can also be severe and limit your ability to move the joint at all. This is not an emergency condition, and can often be managed with home care.
Causes of Sudden Joint Pain
1. Traumatic Fractures
Traumatic or acute fractures caused by direct impact to the bone such as those during a fall, car accident or sports injuries. This will cause the bone to break and can also lead to pain in the extremities or nearby joints.
2. Dislocations
Trauma may cause a bone to move from its normal position in the joint, resulting in a dislocation. Dislocations of the fingers, knee, hips, pelvis and ankle are common and can result in sudden pain while immobilizing the joints.
3. Sickle Cell Anemia
This is a chronic hereditary condition that causes the red blood cells to develop in a crescent or sickle shape because the hemoglobin, a protein that helps to carry oxygen, develops abnormally. This can cause the blood cells to burst, which will lead to anemia. This condition may also cause inflammation, swelling and pain around the joints that can last for a few minutes up to a few days.
4. Septic Arthritis
This is a joint infection caused by fungi or bacteria present in other parts of the body spreading to the joints. This can affect one joint or several, causing sudden, severe pain, swelling and warmth. You may find that it is difficult to move the joint. Ankles, knees, hips, elbows, shoulders and wrists are common locations for this infection.
5. Lupus
The autoimmune disorder lupus causes the immune system to attack the organs and tissues throughout the body. This can result in sudden episodes of stiffness or severe joint pain in the elbows, fingers, knees and shoulders.
6. Gouty Arthritis
Gouty arthritis causes inflammations in the joints that will come in severe attacks, causing the base of the big toe to become very tender, hot, swollen and inflamed. Gout is the result of uric acid crystals building up in this joint, damaging the cartilage.
7. Dengue Fever
This virus is spread by mosquitoes in subtropical or tropic regions to world travelers or those living in these areas. This condition causes high fever and a red rash similar to measles 2.5 days after the fever has begun. This condition can also cause the skin to become very sensitive, muscle aches, fatigue, nausea, headache behind the eyes, swollen lymph nodes, vomiting, nausea and joint aches.
8. Osteonecrosis
This condition is defined as reduced blood flow to the joints and bones, making the bone break down more quickly. Osteonecrosis is particularly common in the upper legs, though the knees, ankles and shoulders can also be affected. Women in their 30s or older are more likely to develop this condition, particularly if they have joint injuries, alcohol abuse, long term steroid treatment, arthritis or cancer in their medical history. At first, those suffering from this condition will not show any symptoms, but as the disease advances, joint pain and immobility will become increasingly severe.
Because there is such a variance in the conditions that could cause sudden joint pain, it is important to visit your doctor to get an accurate diagnosis.
Treatments for Sudden Joint Pain
1. Medications
If your joints are sore but not swollen, acetaminophen can help to limit your discomfort. Those that are experiencing swelling can rely on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, aspirin and naproxen or Cox-2 inhibitors like Celebrex to manage their symptoms. It is important to use these medications sparingly as they can increase your risk of gastrointestinal bleeding or liver damage over time.
Your doctor can prescribe stronger versions of these medications if necessary, but you should discuss potential side effects such as constipation or drowsiness before using them.
2. Topical Agent
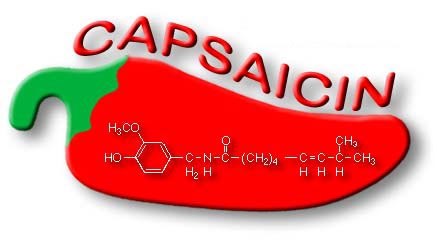
Capsaicin from chili peppers can help to reduce the symptoms of conditions such as arthritis by blocking substance P that transmits pain signals. It will also trigger endorphins that will allow the body to naturally block pain. These creams should be used with care as the capsaicin can cause stinging or burning of the skin. Selecting a brand with methyl salicylate that will cool the skin can help to reduce this risk.
3. Injections
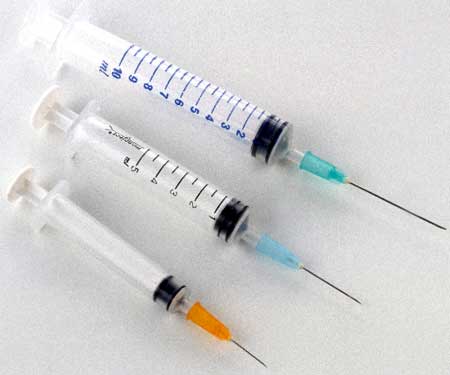
Those that do not get relief from over the counter medications can see their doctor for steroid injections every 3-4 months. These are commonly used to address joint diseases, inflammation or arthritis, but there is no confirmation regarding whether or not this method is effective. Injections can also be used to provide natural joint fluid to treat osteoarthritis or remove fluid from a swollen joint.
4. Physical Therapy
Strengthening the muscles around a painful joint can increase stability so it is easier to get a full range of motion out of the joint. Ultrasounds, electrical nerve stimulation, heat or cold therapy and manipulation can be used during physical therapy.
Those that are overweight will often be encouraged to diet and exercise during physical therapy to take the pressure off of overworked joints. These individuals may need to stick to low impact exercises like swimming or biking that will not make their pain worse.
5. PRICE Method
This acronym refers to protecting the joint with a brace, resting the joint, icing the inflamed area for 15 minute intervals throughout the day, compressing the joint with a wrap and elevating the joint to reduce inflammation and spasms. Avoid taping or immobilizing a joint for too long as this can lead to stiffness.
6. Supplements
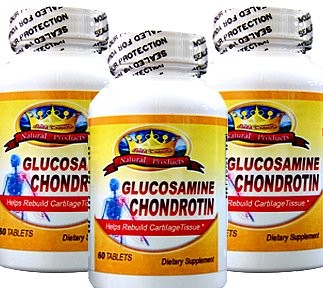
Some have found that chondroitin or glucosamine supplements will reduce joint pain and help to cushion the joints to increase their function. These substances do not have any side effects, but they may not be as effective for all patients.
7. Others
If you are experiencing muscles spasms around the joints, wrapping the joint or applying a heating pad to the area several times a day may provide relief. Your doctor may recommend that you splint the joint to reduce your discomfort, but you should not keep a joint immobilized for long periods of time as this can cause it to stiffen and become difficult to function.
When to See a Doctor
If the sudden pain in your joint also comes with tenderness, warmth, swelling or redness in the area you should speak to your doctor. If you have lost 10 or more pounds without trying, you have a fever without flu symptoms, your joint pain has lasted over 3 days or the joint pain is accompanied by other severe symptoms you should also work with your physician to determine the root cause. Seek emergency care if you notice sudden swelling, you are not able to use the joint, the joint appears to be deformed or you are experiencing intense pain.