Strep throat is a bacterial throat infection. Although it is sometimes considered a sore throat because of the pain, it is different from other sore throats that are caused by viruses. Strep throat is highly contagious and usually affects children and young adults. However, it also affects adults who may experience milder symptoms. Nevertheless, it is important to be able to identify the infection because its treatment differs from other sore throats.
In this article the various stages and characteristics of strep throat will be depicted to help readers identify their infection.
What Causes Strep Throat?
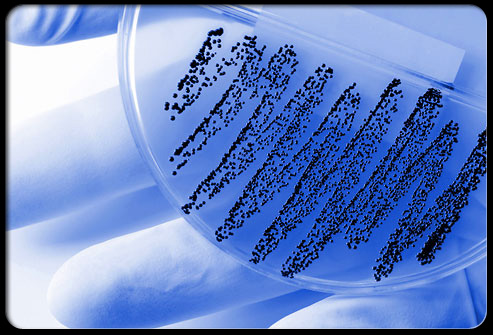
Strep throat is a throat infection that is caused by Streptococcus A bacteria. Although sometimes this disease may be recognized by its symptoms and clinical manifestations, the best way to diagnose it is by taking a throat swab or a rapid strep test. The results of this test are ready in 5-10 minutes, but it may not detect all cases of strep infection. If it is found negative, the doctor may conduct a throat culture. It may take a couple days to obtain results.
A throat culture consists of bacteria from the throat that are grown in the lab. If positive, it will reveal Streptoccocus group A, or specifically Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, growing in the medium.
Stages of Strep Throat
One catches a strep throat infection from close contact with someone else who has it and sneezes, coughs, or talks, releasing droplets of saliva that carry the bacteria. On the first day of infection there may not be symptoms or signs of the disease. However, between the second and the fifth day from infection one may start to feel a scratchy sensation at the back of the throat. In children and young adults it may start as a sudden and severe sore throat that is not associated with coughing, sneezing, or stuffy nose.
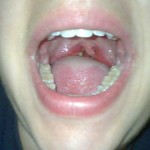
At first one may not see significant changes inside the throat. However, even without obvious changes or symptoms, bacteria may be transmitted to others.
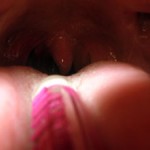
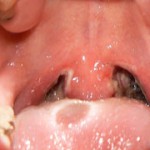
The following day one may see tiny red spots on the palate or ‘roof’ of the mouth. Severe sore throat may be experienced, although it may be mild in adults.
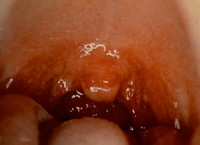
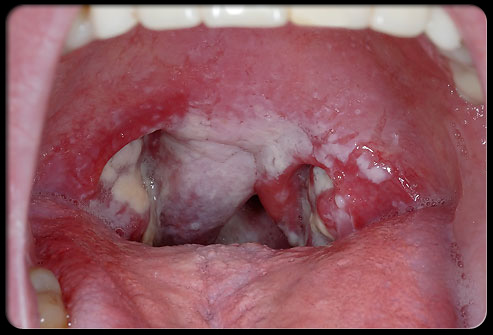
The next stage is marked by the appearance of small white spots on the tonsils that are inflamed. The patient develops high fever and has difficulty swallowing.
The white spots, which represent pus or tonsillar exudates, may increase in the next few days and may become yellowish in color. If left untreated, complications may develop.
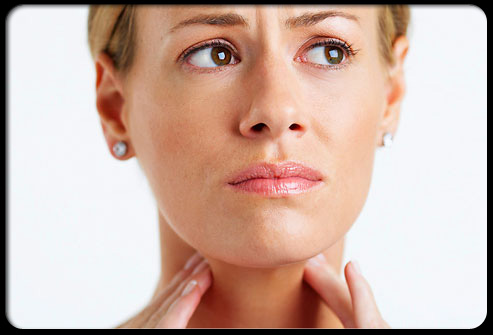
One may also notice swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck.
Between the 5th and 8th day of infection, the third stage develops, and the throat turns grayish in color. The patient experiences pain, which may be accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting (usually in children).
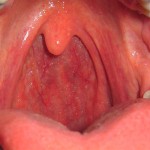
Finally, in the last stage of the disease, which is usually one week after infection, the throat is cleared of pus but remains slightly reddish. Symptoms begin to decline and the throat begins the healing process.
Treatment
When confirmed, streptococcal infection is treated with antibiotics to shorten its course and prevent spread. These antibiotics, which include penicillin, amoxicillin, or cephalexin, must be given within 48-72 hours of infection to be effective. However, some people may choose not to use antibiotics, especially if their symptoms are mild. Sore throat may be relieved with lozenges and fever may be treated with acetaminophen and rest.
If you feel a sudden severe soreness in your throat that is not accompanied by cold symptoms including coughing or sneezing, consult a doctor for early treatment as strep throat is highly contagious. Forgoing treatment can also lead to complications such as ear infection, sinus infection, peritonsillar abscess, rheumatic fever, or kidney disorder.
Watch out for drooling and difficulty breathing in children, which are danger signs requiring emergency treatment.