There can be many reasons as to why a person has stomach pain after eating. Overeating, eating spicy food excessively, or being stationary after eating are some of the causes of stomachache after eating. However, the real cause may go deeper than these reasons. The abdominal cavity consists of not only the stomach but many other vital organs. For example, the oesophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, cecum, and the appendix make up the digestive tract. The liver, pancreas, and gall bladder are the accessory organs that aid in the digestion of foods. The urinary tract organs such as the kidneys and the ureters are also contained in the lower abdominal region. The spleen is another organ located in the same cavity area. Problems with any one of these organs can also be associated with pain after meals.
Types of Stomach Pain
The stomach consists of different areas that divide in to five different parts. These are the Cardia, the Fundus, the Corpus, the Pylorus, and the overall Antrum.
The cardia is the region to which the oesophagus releases the consumed food. The fundus forms the upper curved part of the digestive system. The corpus area contains the central section with intestines and other key organs. The pylorus acts on emptying the stomach contents to the small intestines. The type of pain associated with the stomach will depend on which part of the stomach the pain is generating. Pain in any of these areas is not to be considered lightly as the underlying cause can be life threatening.
Causes of Abdominal Pain after Meals
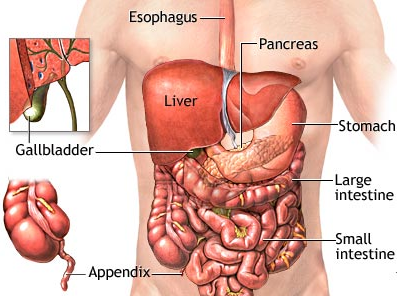
- Appendicitis - The appendix is a small sac which is attached to the large intestine. This is an organ which plays an important role in the immune system as it is rich in lymphocytes. A person with an inflamed or enlarged appendix might not be aware of this situation without a medical check up. Such patients experience excruciating abdominal pain in the lower right side of the stomach after meals.
- Gallstones - The gallbladder is below the liver in the right upper stomach area. Gallstones form due to the hardening of bile that is stored in the gallbladder. Gallstones can range from the size of small grains of sand to the size of a golf ball. Pain in the upper right abdomen that spreads to the right upper back and right shoulder and chest area can signify gallstones. The pain is generally experienced after meals.
- Pancreatitis - Situated behind the stomach, the pancreas assists with the digestion process of food. When the pancreas is inflamed, digestive enzymes secreted in the pancreas will attack and damage the tissues before the food can reach the small intestines. Gradual or sudden pain in the upper section of the stomach after meals is a sign of pancreatitis.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) - PID occurs when any one of the reproductive organs such as uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries are inflamed due to an infection. There are many types of bacteria that can cause PID. The most common are those that are transferred during sexual intercourse. Pain in the lower abdomen area after eating is a common symptom of PID.
- Intestinal Obstruction - This can be a blockage in the small intestines or colon, which prevents consumed food from passing through. Obstruction of the intestines could be due to adhesions in the abdomen, tumours, or hernias. Symptoms such as cramps after meals, watery stools are tale tell signs of intestinal obstruction.
- Lactose intolerance - This is an allergy that is caused by certain dairy products. This is the body’s inability to digest and metabolize lactose. In those people with lactose intolerance, the stomach hurt after eating and the abdomen area gets bloated.
- Diverticulitis - This is caused by weakness which develops in certain points of the muscle of the colon. These weak points lead to diverticula which traps certain particles of stools. With the entrapment of stools, the diverticula can become inflamed. This will cause stomach pain after eating followed by stomach cramps and tenderness in the lower left side of the stomach.
Apart from above mentioned serious issues, stomach hurt after eating can be due to simple reasons such as too much water intake after meals, an infection, gastritis and acid reflux as well.
Prevention and Treatment of the Stomach Pain after Eating

The prevention of stomach ache after eating will depend on the type of pain. Therefore, if the stomach pains persist, individuals will have to obtain a proper diagnosis as to the cause of the pain. A health care provider will then be able to prescribe the right treatment and medication in order to avoid pain in the stomach after meals. In most cases, change in diet and personal behaviour will suffice for the alleviation of pain in the stomach after meals. If stomach pain is due to an ulcer or acid reflux, antacids may be prescribed. In the cases of appendicitis and hernia, surgery may be the only answer. Whatever the type of pain, it is always recommended that medical attention be considered in order to avoid any complications, which can arise if stomach pain after eating is ignored.
Stomach pain is one of the most common ailments that plague people of all ages. From infant colic to adult appendicitis, a vast range of medical conditions and illnesses can cause pain in various regions of the stomach. Some pains are persistent and continue without respite, and other pains materialize when a meal is consumed. Such distinctive features and place of pain origination can help pinpoint the root cause of pain.