Stomach flu is also known as viral gastroenteritis. This simply refers to inflammation and swelling of intestines and the stomach due to a viral infection. This flu is caused by consumption of contaminated food or drinking contaminated water. It has been termed as the leading cause of diarrhea. Symptoms are experienced at least four hours after infection. They include diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Others include fever, poor feeding, sweating, muscle pain and weight loss.
How to Get Rid of Stomach Flu
1. Take Medications
- OTC Painkillers. This includes over the counter medication. This can be helpful if you experience severe stomach aches. Most ideal painkillers can be acetaminophen, aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen among other combinations. Aspirin should not be taken by those under the age of twenty, and it is ideal to eat before taking medication.
- Diuretics. These should not be administered before consulting with a medical practitioner. Patients under diuretics can develop diarrhea requiring them to stop using the diuretics. Remember not to stop taking prescription medication before consulting with your doctor.
- Anti-diarrhea Drugs. Diarrhea is a serious cause of dehydration which can be fatal. Anti-diarrhea medication will stop the diarrhea and should not be administered without the consent of a healthcare provider. Avoid giving anti-diarrhea medication to children unless you are instructed to do so by a doctor. In case of bloody diarrhea, severe diarrhea or fever, do not use this medication before consulting a medical practitioner. And do not administer this medication to children.
- More Tips. Stomach flu is caused by viruses, not bacteria. Antibiotics cannot be used to treat stomach viral infections. Do not take them at all.
2. Rehydrate
The worst kind of stomach flu causes dehydration. Fluids can be lost through diarrhea or vomiting.
- Fluids to Avoid. Avoid alcohol, fruit juice including apple juice, acidic fluids like lime or orange juice, caffeine and milk. You should also avoid flat or bubbly cola or sodas, broth or even jell-O. They contain too much sugar that worsens the diarrhea without replacing minerals.
- Fluids to Have. Drink lots of fluids, including sports drinks, water and electrolyte solutions that are very important. The electrolyte solutions can be purchased at pharmacies. Adults and older children can take sports beverages like Gatorade but should never be used on younger children. Fluid and electrolyte solutions or even freezer pops are most ideal for young children and infants and can be bought at drug and food stores.
- Homemade Rehydration Solution. You can make your own rehydration solution if for one reason or the other you cannot reach a drug store. In order to make your own rehydration solution, mix the ingredients of one liter (4.25 cups) of clean water, 30ml (6teaspoons) sugar and 2.5ml (0.5 teaspoon) salt and then take them in large quantities.
- More Tips. Take in minimal fluid amounts after every half hour or one hour. Forcing too much fluid can induce vomiting causing more dehydration. For small children and infants, make use of syringes or teaspoons. Add more fluids to the baby formula or breast milk. There is no need to switch to soy formulas. For diarrhea patients who are unable to take the fluids orally, intravenous methods (through veins) can be used to induce the fluids. This can be helpful in younger children who suffer a higher risk of dehydration. Parents should take the time to monitor the number of diapers they change per day on their sick children.
3. Eat Bland Foods
- Foods to Eat. Eat foods that do not require too much digestion. This will ease the stomach irritation. These foods include BRAT diet (bananas, rice, apples and toast) and ensure that foods are offered in small quantities often. Some foods you can eat include bread, cereals, lean meat, potatoes, fresh apples, plain yogurt and vegetables.
- Foods to Avoid. In case of frequent vomiting, avoid uncomfortable or irritating foods such as spicy foods, fatty foods and chips.
4. Try Natural Remedies
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
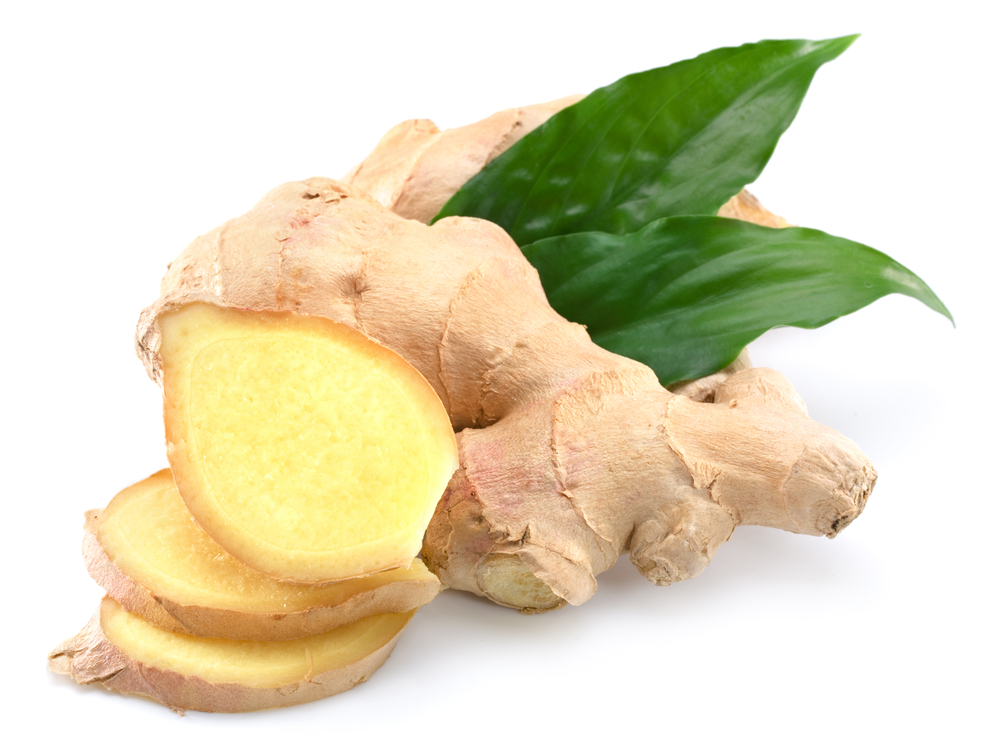
| Ginger |
Ginger contains anti-inflammatory agents, which aid in digestion and nausea. You can take ginger capsules, ginger ale or ginger tea. You can also chew the ginger root. |
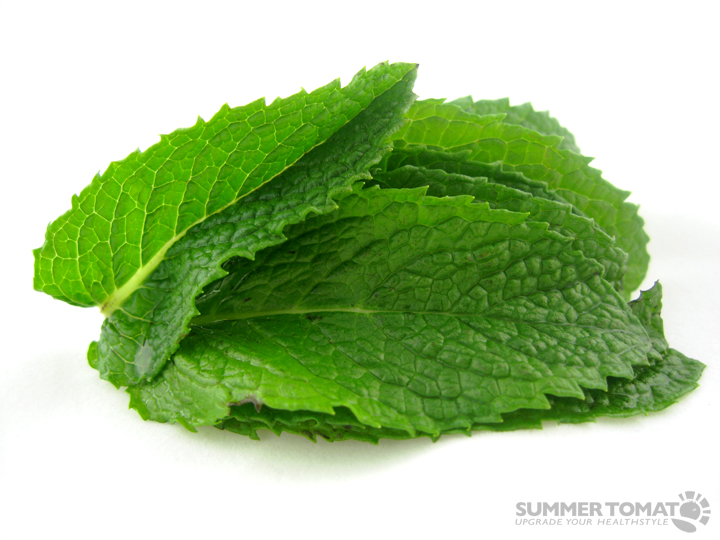
| Mint |
This can be used for an upset stomach. Reduces the symptoms associated with irritable bowel syndrome and indigestion. Calm the stomach by chewing peppermint gum or take peppermint tea. |
| Tea |
Chamomile and rooibos (red) tea can calm the digestive track easing stomach cramps. Chamomile can also soothes the stomach. |
| Probiotics |
These are organisms that replenish the useful gut bacteria. This brings balance to the digestive system. Your doctor can help you choose depending on your condition. These organisms can be found in kefir and yogurt. |
5. Rest and Sleep
Adequate sleep is important during the stomach flu healing period. The recommended sleep time is between eight and ten hours daily. If you have a sick off from work or school, try taking naps in the afternoons. While it may be tempting, avoid taking sleep aids when still unwell or vomiting. You should also, avoid sleeping when lying on your back.
When to See a Doctor
For Adults
Adults should contact their doctor if they experience symptoms like:
- Cannot keep liquids down for twenty four hours
- Vomiting for more than 2 days
- Vomiting blood
- Dehydration signs like dry mouth, severe thirst, no or minimal urine, dark yellow urine as well as dizziness and weakness
- Blood in bowel movement
- Fever above 40 degrees C
For Children and Infants
Take your child to the doctor if you notice symptoms like:
- Fever above 38.9 C or above
- Irritability and tiredness
- Discomfort and pain
- Blood diarrhea
- Dehydration signs like urinating and drinking more fluids than normal
For infants, spitting out is normal, but vomiting is a sign of concern. Seek medical attention if you notice vomiting. Contact your pediatrician if:
- The child has been vomiting for hours.
- The infant has not wet the diaper in more than six hours.
- They experience diarrhea and blood in stool.
- You notice the sunken fontanel which is the soft spot on the baby’s head.
- They cry without tears and dry mouth.
- They are abnormally drowsy, sleepy and unresponsive.