Stools that are hard are normally a result of a condition known as constipation. When the stools remain in the GI tract for more than 48 hours, any fluid contents in them was reabsorbed by the body. This causes the stool to become dry, hard and difficult to pass from the body. In exceedingly severe cases it may cause pain and bleeding while passing these stools. In the majority of cases, all it needs is a few home therapies. But in serious cases, it is vital to visit your doctor and understand the root cause.
How to Soften Hard Stools
1. Home Remedies
In many cases, some change in your diet and lifestyle can get rid of indicators of constipation. Less often, you may need medical treatment. Above all, recognize that a successful treatment program can take time and effort.
High-Fiber Diet. Add high-fiber (20g to 35 g of fiber) foods into your diet every day, which can help the body form soft and bulky stools. Following displays some foods rich in fiber.
| Category | Food |
|---|---|
| Bread |
Granola bread, wheat bran muffins, whole wheat bread, Nutria-Grain waffles, popcorn |
| Cereal and Grains |
Raisin Bran, Bran Flakes, Frosted Mini Wheat’s, Shredded Wheat, Oatmeal, Muslim, Bran Buds, All-Bran, Fiber One, 100% Bran, Corn Bran, granola, oat bran, brown rice, rye bread, multigrain |
| Vegetables |
Artichoke, beets, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cabbage, carrots, green peas, green beans, sweet corn, acorn, spinach, butternut squash, potatoes with skin, turnip greens |
| Legumes |
Lentils, baked beans, garbanzo beans, black-eyed peas, lima beans, pinto beans, kidney beans, chili with beans |
| Fruits |
Avocado, apples with peel, banana, oranges, papayas, nectarines, kiwis, pears, blackberries, raspberries, mangos, strawberries, cooked prunes |
| Others |
Peanut butter, trail mix, almonds, pistachio nuts, pecans, dried figs, sunflower seed kernels, tomato paste, applesauce, raisins, dates |
Regular Exercise. Physical activity can help stimulate intestinal activity.
Fluid Intake. Drink plenty of water and other fluids will help soften your stool
Bowel Movements. Have sufficient time to allow undisturbed visits to the toilet. Don't ignore the urge to have a bowel movement.
2. Alternative Therapies
There are several alternative approaches that might also provide relief, although they have not been extensively studied.
Massage. Massage works by compressing, manipulating, and stretching the skin, muscles, and joints. Techniques include acupressure and shiatsu. When useful to the abdominal area, massage might help relax any muscles that support the bladder and intestines and this helps promote activity of the bowel.
Acupuncture. This traditional Chinese medicine involves the manipulation and insertion of very fine needles in various areas of the body. This therapy might help stimulate the colon and also can release any pain from constipation, although it is efficacy for this has not been shown.
Homeopathic Remedies. This is nontoxic, holistic, method of medicine that’s customized to the symptoms. Frequent homeopathic therapies exist for constipation and they habitually consist of laxative that is plant-based. But, just because they are natural does not mean they are safe. For instance, many herbal extras are linked with potential unsafe drug interactions and side effects. Also it is advised to talk with your physician before trying a homeopathic remedy.
3. Medical Treatments
Laxatives. Laxatives contain chemicals which help add the stool motility, frequency and bulk – thus temporary relieving constipation. But, when overused or misused, they often cause problems such as chronic constipation. Others include stool softeners or emollient laxatives such as Colace that contain a surfactant that keeps the stools ‘wet’ and soft. These do often take a week or so to work and are used frequently by those recovering from surgery.
Other Medications. Other medications can include the agent lubiprostone or Amitiza and are available by prescription. These increase fluid content of stool. They are called chloride channel activators. 5-HT-4 agonists which have agents stimulate release of compounds in the body that will increase fluid secretion in the intestines and decrease colonic transit times. These are drugs that are not available in the United States as there are some concerns about their safety.
Surgeries. Surgeries can be done when the constipation is chronic and severe and no other treatment has helped. This consists of removing the problem segment or segments of the anal sphincter or rectum.
Treating Potential Diseases. This is aimed at other specific causes. One of these can be pelvic floor dysfunction and your physician will suggest biofeedback as the treatment. This retraining method will help the person to learn to better coordinate muscles used when having a bowel movement.
Causes of Hard Stools
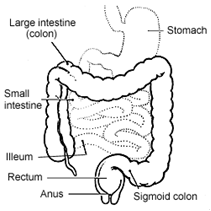
To really understand what causes hard stools, you need to first acquaint some understanding of how the digestive system works. After most of the nutrients from food we eat is absorbed by the smaller intestine, it then discharges fiber and liquid to the larger intestine and it is there the substances go through a progression of being molded into stools. As the fecal material moves from end to end of the larger intestine, fluid is drained out; creating a stool that is set to be emptied when having a movement of the bowel. Fluid can be drained out from fecal matter that is present for too long in the lower part of the large intestine, resulting in the development of really hard, dry stool. So it makes sense that the most common reason of hard stools is irregularity of bowel movements causing constipation.
To a smaller point, hard stools may be produced by insufficient fluid intake, as the colon is required to draw excess water from the stool. Stools that are hard may also be the consequence of an inadequacy of dietary fiber in the diet. Other causes include pregnancy, medication, digestive disorders such as IBS and Crohn's disease, and medical conditions such as hypothyroidism.
When to See a Doctor
Constipation might be bothersome, but it is normally not serious – in fact the majority of people with constipation do not need to seek care from a physician. But, chronic constipation might lead to complications or be a sign of some type of underlying problem.
But do see your physician if you have an unexplained onset or change in bowel habits or if symptoms are severe and last longer than 3 weeks. Also seek medical care if you experience any of the following:
- Bowel movements more than 3 days apart, in spite of changes in exercise or diet
- Extreme pain in abdomen
- Thin or pencil-like stools
- Bloody stool
- Constipation alternating with diarrhea
- Pain in rectal area
- Unexplained Weight loss
Any of these symptoms could be indicators of something that is more severe.